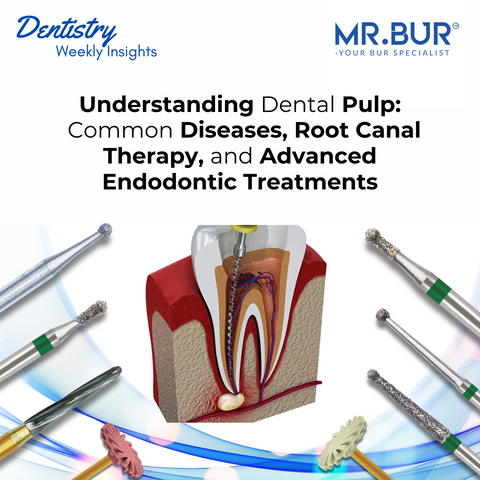
When a tooth’s pulp is compromised due to deep cavities or trauma, dentists must decide on the best treatment to preserve oral health. Pulpotomy, Root Canal Therapy (RCT), and Extraction are the 3 primary solutions. But which one is the right choice? This article dives deep into pulpotomy, its advantages, and how it compares to RCT and extraction.
What is Pulpotomy?
Pulpotomy is a vital pulp therapy primarily used in primary (baby) teeth and young permanent teeth with open apices. It involves removing the infected coronal pulp (the top portion inside the pulp chamber) while leaving the healthy root pulp intact.
When is Pulpotomy Recommended?
A pulpotomy is ideal when:
-
There are asymptomatic deep caries close to the pulp.
-
The tooth has no signs of infection (no swelling, sinus tracts, or abscess).
-
The inflammation is limited to the coronal pulp, while the root pulp remains healthy.
-
The tooth needs to be preserved for normal development in children.
Procedure of a Pulpotomy:
-
Anesthetize the tooth and tissue
-
Isolate the tooth with a rubber dam
-
Remove caries with a high-speed straight bur without entering the pulp chamber
-
Mr. Bur Round Diamond Bur – Efficient for caries removal while preserving healthy dentin.
-
Remove the roof of the pulp chamber with
-
Mr. Bur Endo Access Bur (Endo-Z) – Facilitates smooth and accurate access to the pulp chamber.
-
Remove coronal pulp with
-
Mr. Bur Pulp Chamfer – Efficient in coronal pulp tissue removal with minimal vibration.
-
Apply formocresol with a pledget of cotton and leave it for 4 minutes.
-
Remove formocresol pledget and check if hemorrhage has stopped.
-
Fill the pulp chamber with Zinc Oxide Eugenol cement
-
Restore the tooth with a stainless steel crown
-
Mr. Bur Crown and Bridge Preparation Kit FG – Ideal for crown preparation, refining margins, and achieving a smooth surface.
-
Mr. Bur Composite Polishing Diamond Polisher
– Ensures precise adjustments before cementing the stainless steel crown.
Success Rate & Alternatives to Pulpotomy:
-
Indirect Pulp Capping (IPC): If the pulp is not exposed, a medicament is applied to avoid exposure.
-
Direct Pulp Capping (DPC): If the pulp is minimally exposed, it can be covered with biocompatible material instead of pulpotomy.
Visit to Know the Step-by-Step Procedure for Pulp Capping: Understanding Dental Pulp: Common Diseases, Root Canal Therapy, and Advanced Endodontic Treatments
Pulpotomy vs. Root Canal Therapy (RCT) vs. Extraction: Key Differences
|
Feature |
Pulpotomy |
Root Canal Therapy (RCT) |
Extraction |
|
Indication |
Reversible pulpitis, deep caries in primary or young permanent teeth |
Irreversible pulpitis, necrotic pulp, periapical infection in permanent teeth |
Non-restorable tooth, severe infection, systemic risk |
|
Procedure |
Partial removal of pulp, medication application, and restoration |
Complete removal of pulp, cleaning, shaping, filling canals, and final restoration |
Tooth removal with or without replacement (implant, bridge, denture) |
|
Tooth Preservation |
Tooth remains vital, allowing continued root development |
Tooth structure remains but becomes non-vital |
Tooth is permanently lost |
|
Pain & Healing |
Minimal discomfort, faster healing |
Some post-procedure pain, longer healing |
Immediate healing but requires a replacement for function |
|
Commonly Used In |
Children (Primary Teeth) or immature permanent teeth |
Permanent Teeth with irreversible pulpitis |
Both primary & permanent teeth that cannot be saved |
|
Long-Term Success |
High success in primary teeth if properly restored |
Long-lasting with a proper crown |
Requires artificial tooth replacement for function |
When is Extraction a Better Option?
While pulpotomy and RCT aim to save the tooth, extraction is sometimes unavoidable.
Extraction is recommended when:
-
The tooth has extensive decay beyond restoration.
-
There is less than 2/3 root length remaining (in primary teeth).
-
There are multiple teeth requiring pulp therapy, making extraction more efficient.
-
The patient is immunocompromised (e.g., congenital heart disease) and at risk of infection.
-
The tooth shows signs of internal resorption.
Types of Extraction Management Options:
-
Local Anesthetic (LA) – for cooperative patients.
-
Inhalation Sedation (RA) – mild sedation for anxious patients.
-
General Anesthesia (GA) – for multiple extractions or uncooperative children.
Risks of General Anesthesia in Extractions:
-
Fatality risk: ~1:40,000.
-
Side effects: Nausea, dizziness, pain, and tiredness.
-
Prevention of repeat anesthesia: Proper planning ensures all necessary extractions are done in one session.
Other Advanced Treatment Options for Pulp Disease
1. Apexogenesis (For Immature Permanent Teeth)
-
Used when pulp is inflamed but still vital.
-
Encourages continued root development.
2. Apexification (For Non-Vital Immature Permanent Teeth)
-
Used when pulp is necrotic, and root development is incomplete.
-
Induces hard tissue formation at the apex.
3. Regenerative Endodontic Therapy (RET)
-
Used for necrotic young permanent teeth with open apices.
-
Stimulates pulp regeneration using biomaterials.
4. Lesion Sterilization and Tissue Repair (LSTR) for Primary Teeth
-
A non-invasive approach for pulp infection in primary teeth.
-
Uses antibiotic pastes (Metronidazole, Ciprofloxacin, Minocycline) to sterilize pulp tissue.
Final Verdict: Which Treatment is Right for You?
Choosing between pulpotomy, root canal therapy, and extraction depends on several factors: If the pulp is inflamed but still healthy → Pulpotomy (ideal for children’s teeth). If the pulp is irreversibly damaged but the tooth is restorable → Root Canal Therapy. If the tooth is non-restorable, severely infected, or poses health risks → Extraction.
Key Takeaway:
Pulpotomy is an excellent choice for saving children’s teeth and preventing premature extractions. However, in permanent teeth, root canal therapy offers a long-term solution, while extractions should be considered only as a last resort. Consulting with a dentist will ensure the best treatment plan based on the tooth condition, patient’s age, and long-term prognosis.
Diamond Burs, Carbide Burs, Surgical & Lab Use Burs, Endodontic burs, IPR Kit, Crown Cutting Kit, Gingivectomy Kit, Root Planning Kit, Orthodontic Kit, Composite Polishers, High Speed Burs, Low Speed Burs